AI for Business | Business for AI (ABBA): Cross-University Modular Offerings for the AI Competency Development of Business and Economics Students
- Contact:
- Project Group:
- Funding:
BMBF
- Partner:
University of Hohenheim, University of Bayreuth, University of Applied Sciences Frankfurt
- Startdate:
1.12.2021
- Enddate:
30.11.2024
As part of the project ABBA (AI for Business | Business for AI), we educate students how to embed Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies in AI-based Information Systems to create business value. A specific focus of the project is to establish an AI Learning Factory (KI Lernfabrik) that supports augmented hybrid learning.
The Project
Applying artificial intelligence (AI) in business contexts requires skills and knowledge. The need for understanding AI to integrate it in business can be reflected in many scenarios including evaluation of technical systems, optimization of operational processes, improvement of work environments and so on. Such a need can be fulfilled by empowering business students with effective educational approaches and resources. The aim of the joint project is to develop and provide a teaching module kit for AI that provides business students with scientifically sound and practical AI skills.
In the scope of this project, we work jointly with researchers from other universities to contribute in the following topics:
- Open Code & Open Data
- AI Learning Factory
- StudyBuddy Chatbot for AI Education
ABBA Summer School: Biosignal-Adaptive GenAI Systems
From September 23rd-25th, the research groups of Prof. Mädche and Prof. Weinhardt invited stduents for the ABBA Summer School Seminar at the KD²Lab.
This immersive summer school seminar was offered as part of the ABBA project, focusing on providing students with hands-on experience in designing innovative biosignal-adaptive GenAI systems. The event presented a valuable opportunity for students to explore the potential of biosignal sensors and Generative AI technologies in creating adaptive, user-centered solutions.
This intensive three-day program was designed for both bachelor’s and master’s students with an interest in biosignal-adaptive systems, and a total of 19 students participated. Through a combination of introductory lectures and practical group work, students learned the core methodology of human-centered design and applied it to their own projects. In the introductory lecture, Prof. Mädche provided students with an overview of biosignal-adaptive systems, highlighting their potential to support users in various contexts and addressing the research gap in combining these systems with GenAI technologies.
For the group work, two primary topics were available to students: literature research and programming. These topics were selected to address real-world user challenges, enabling students to apply what they learned in realistic scenarios. After selecting their topics of interest and forming four groups, students explored how to combine biosignal-adaptive sensors with GenAI technologies, such as Large Language Models (LLMs), to create interactive design prototypes aligned with human-centered design principles. On the final day, each group presented their prototype, showcasing their ideation process, design outcomes, study design, and receiving feedback from the audience.
AI Learning Factory
The AI Learning Factory provides a unique learning experience to students. The purpose of the Learning Factory is to supplement traditional university learning formats (lectures, exercises, tutorials) with digital learning content. Here, innovative technologies such as MR and VR are used to enable more interactivity and immersion in learning.
In addition to technical skills (e.g. AI), interdisciplinary and transferable skills (e.g. empathy, self-regulation, communication) are playing an increasingly important role in university studies. Here, we plan to offer related learning modules addressing this trend as well.
The learning factory has been used to support teaching activities (e.g. Business Intelligence Systems Lecture) by offering students an immersive excursion, covering lecture-related topics. We have offered immersive excursions in the following teaching activities:
- WS22/23 Business Intelligence Systems Lecture
- SS23 Foundations of Interactive Systems Lecture
- WS23/24 Business Intelligence Systems & Engineering Interactive Systems Lecture
- SS24 Foundations of Interactive Systems Lecture & Designing Interactive Systems
- WS24/25 Business Intelligence Systems & Engineering Interactive Systems Lecture
Immersive Learning Applications
In our learning factory, we present students different interactive and immersive applications for AI-related topics. We leveraged different technologies such as mobile AR and head-mounted MR displays to present these applications. Here are some examples:
Learn Neural Networks (Virtual Reality - Varjo-XR3)
The application is built with the goal of helping the user to understand and grasp concepts of neural networks. As we purposely recruited students without knowledge in AI, one of the conducting researchers escorts the user through the application by providing the necessary information and background in real time. The application has multiple different interaction formats, ranging from simple multiple-choice questions, over assignment tasks, to building a simple neural network and calculating the forward pass.
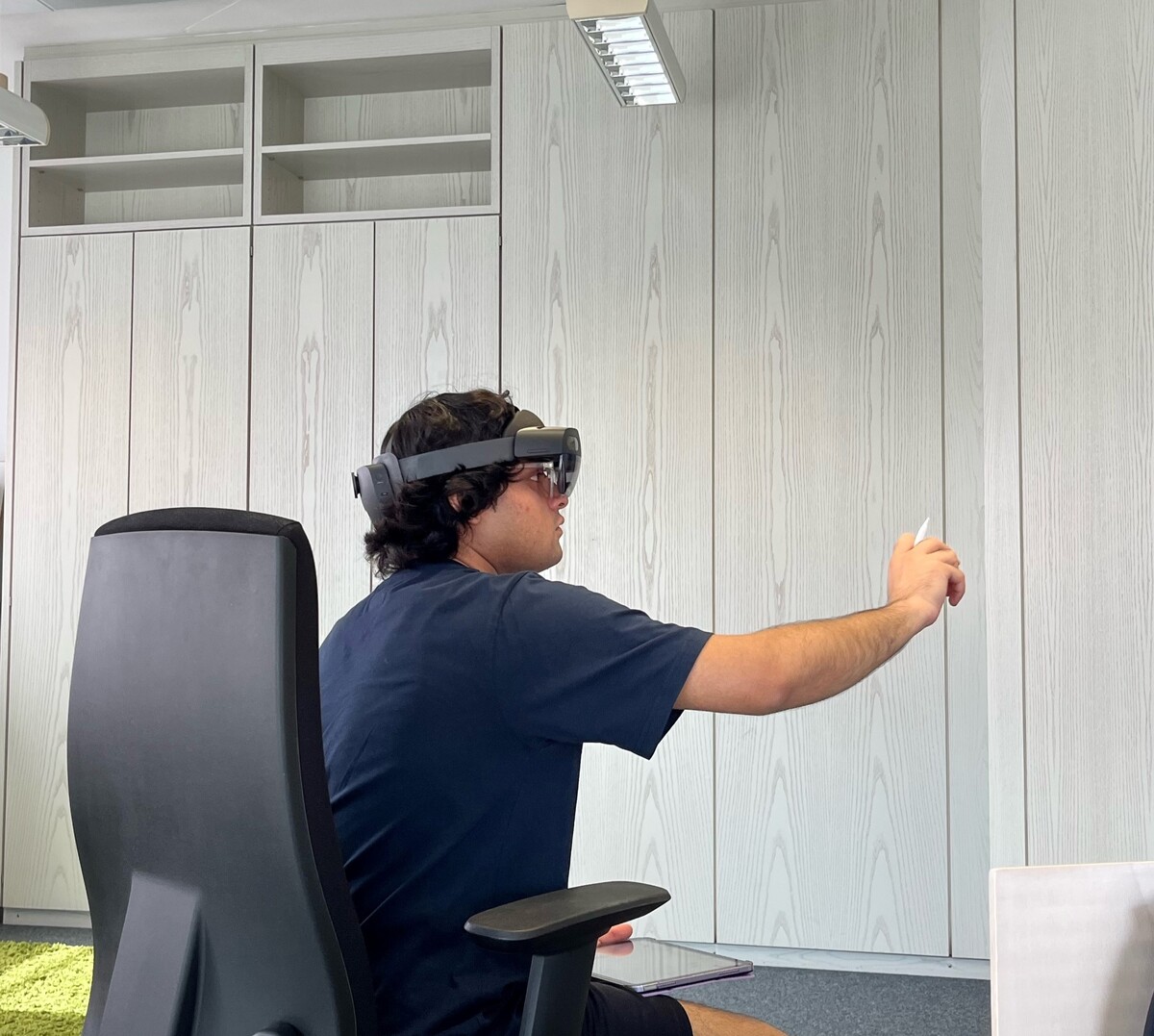
Learn Human Information Processing (Mixed Reality - HoloLens)
This HoloLens application teaches the concept of human-information processing, based on the model human processor concept proposed by Card in 1981. The goal of teaching human-information processing is to support learners in understanding the fundamental principles of human-AI interaction.
Learn ID3 Decision Tree (Mixed Reality - HoloLens)
The MR learning system presents the entropy and information gain users. Users sort out the physical tennis balls and build a decision tree, learning the ID3 algorithm in an embodied approach.
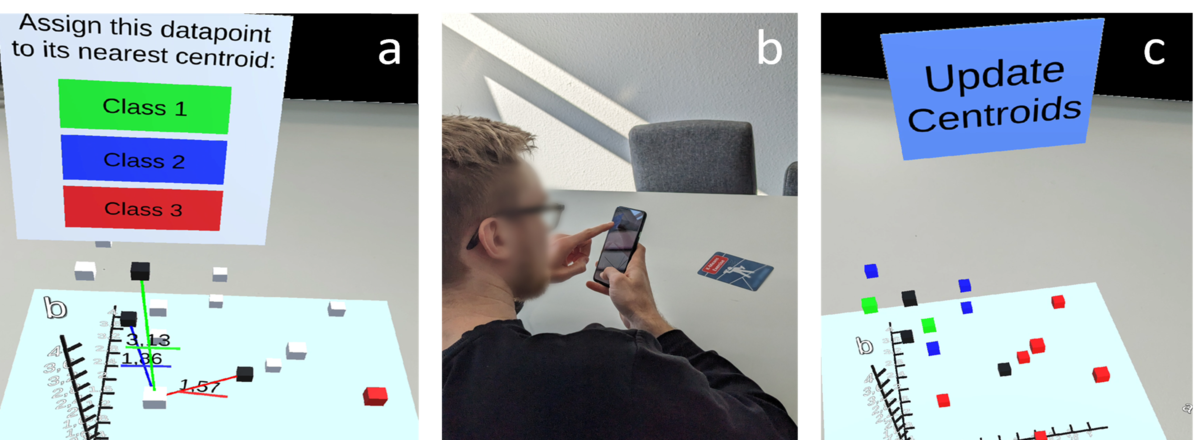
Learn K-means Clustering (Mobile AR)
The mobile AR app presents the distance of a selected data point to each of the centroids. Users assign all data points to their nearest centroid, acting as the K-means algorithm.
StudyBuddy
Apart from the improving AI-related technical competences in the physical learning factory, we provide virtual tools for transferrable skills that are independent of the location and time. Here, we designed StudyBuddy, a personalized chatbot for self-regulated learning.
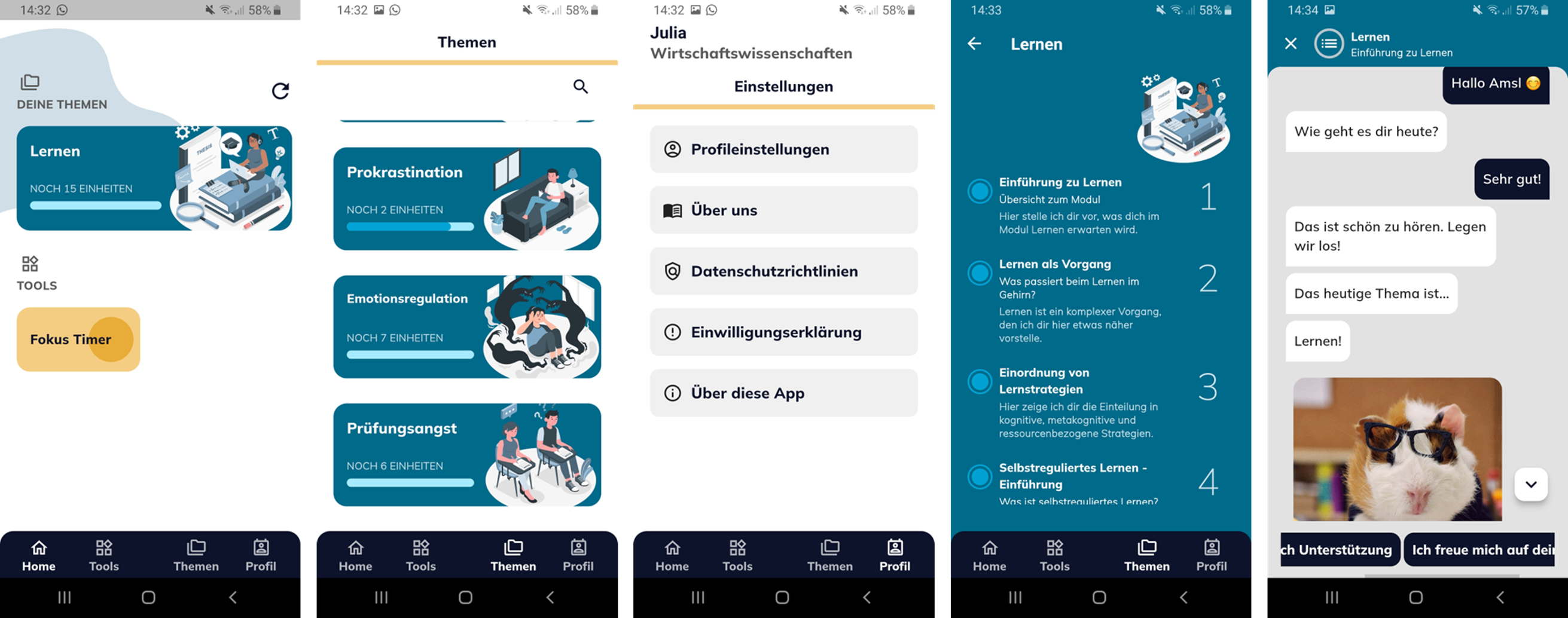
StudyBuddy Chatbot for Self-regulated Learning
Field Studies
As part of the ABBA project, we collaborate with companies and organized field studies in different AI-related areas. The goal is to offer hands-on experience and learning activities for students to apply the theoretical knowledge to a real-world use case. Over the past semesters, the following AI field studies have been organized:
- In SS24, we organized a field study with EnBW with students from the Designing Interactive Systems: Human-AI interaction (DIS) lecture. The project was conducted as part of the DIS master lecture offered by Prof. Mädche and Julia Seitz and carried out in cooperation with EnBW. Over a period of three months, 38 students worked in teams on a real-world challenge provided by our industry partner EnBW. The overall goal and topic of this year’s project was to create innovative design solutions for generative AI-based assistants that support customers of EnBW. The results of all eight groups were well-received by the EnBW topic owners Christian Wendrock-Prechtl and Achim Reuther, as well as the lecture team.
- In SS24, as part of the bachelor lecture "Foundations of Interactive Systems" of the human-centered systems lab, students worked in teams on the project, which allows students to apply the theoretical knowledge learned in the lecture to a real-world use case. In this summer semester, the field study was executed in cooperation with SAP SE and focused on applying the human-centered design process to design an app that supports the achievement of a Sustainable Development Goal (SDG), such as reducing food waste (SDG 2), increasing gender equality (SDG 5), or reducing carbon footprint (SDG 13).
- During the "Business Intelligence Systems" lecture conducted in WS23/24, students worked in a team with real-world use cases and data in order to create a prototypical Business Intelligence & Analytics system using state-of-the-art technologies. The field study was carried out in cooperation with Porsche with a specific focus on sales planning. Students were asked to analyze sales data and develop forecasting models as well as analytical dashboards leveraging visualization and explanations.
- In the lecture of "Engineering Interactive Systems" conducted in WS23/24, students collected data and designed adaptive operator management systems leveraging the collected biosignal & interaction data. Furthermore, the student teams analyzed this data, developed models, and suggested designs of biosignal-based adaptive interventions.
- In the scope of the bachelor lecture "Foundations of Interactive Systems" in SS23, students followed the human-centered design process to develop an idea and design for a new writing assistant that leverages the capabilities of large language models such as OpenAI ChatGPT.
- In the DIS lecture in SS23, over a period of two months, 40 students worked in teams on a real-world challenge provided by our industry partner EnBW. The overall goal and topic of this year’s project was to create innovative design solutions for multiple use cases of ChatGPT in EnBW processes (e.g., ChatGPT as a product guide, conversation management for call center agents and conversation personalization, support for data workers, learning, or legal texts).
- In the BIS lecture conducted during WS22/23, 35 students worked in 8 teams with real-world data and corresponding use cases provided by our industry partner Bosch. The overall goal and topic of the capstone project was to create innovative analytical solutions supporting data-driven decision making at Bosch. Overall, four different use cases were tackled by the teams. The students leveraged different BI&A technologies and commercial systems, e.g. Python, KNIME, and Microsoft PowerBI.















